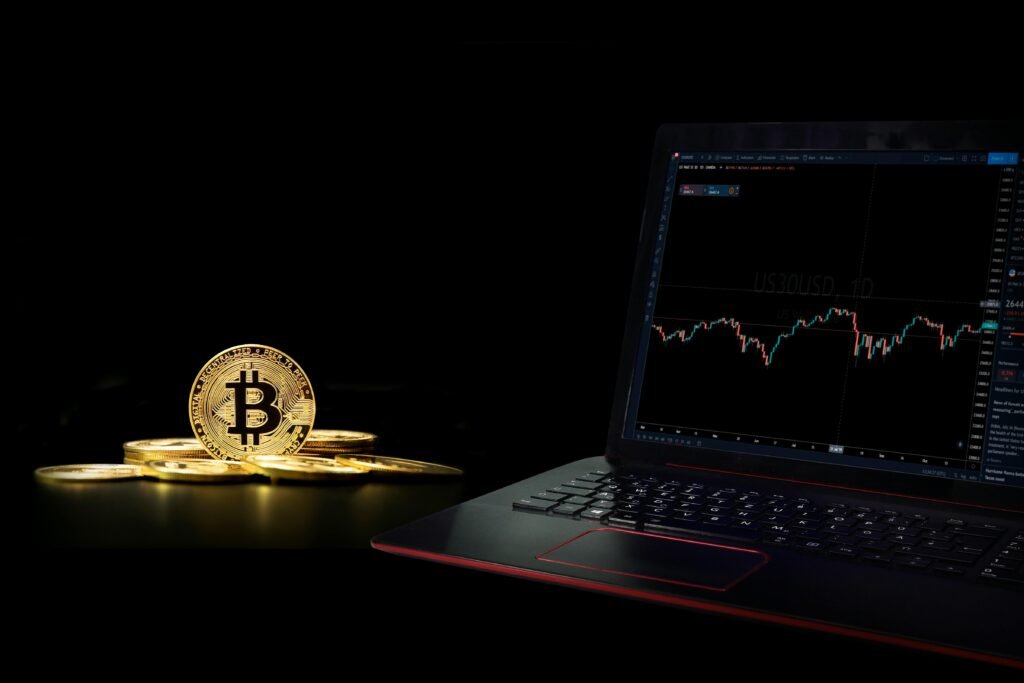
Welcome to the fascinating world of decentralized applications, or DApps. In recent years, DApps have revolutionized the way we think about technology and the internet. They promise a future where control is in the hands of users rather than centralized entities. Intrigued? Let’s dive into what DApps are all about and how they’re making waves in the tech world.
What are Decentralized Apps (DApps)?
DApps, or decentralized applications, are digital applications or programs that exist and run on a blockchain or peer-to-peer network of computers instead of a single centralized server. This decentralization ensures that no single entity has control over the entire network, promoting transparency and security.
In exploring the vast landscape of decentralized applications (DApps), the focus has primarily been on their structure, advantages, and challenges. However, there is a unique aspect that is often overlooked: the role of DApps in environmental sustainability. This is an emerging area where DApps can have a significant positive impact, yet it is rarely discussed in depth.
DApps and Environmental Sustainability
1. Energy Efficiency Initiatives
Traditional blockchain platforms, particularly those using proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanisms, are notorious for their high energy consumption. However, DApps built on more energy-efficient blockchains, such as those using proof-of-stake (PoS) or delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS), are paving the way for greener alternatives. These platforms significantly reduce the carbon footprint of decentralized applications, promoting more sustainable practices in the blockchain industry.
2. Supply Chain Transparency
One of the most promising applications of DApps in sustainability is in enhancing supply chain transparency. By utilizing blockchain technology, DApps can track the provenance of goods, ensuring that materials are sourced sustainably. For instance, a DApp can verify if a product is fair trade or if the raw materials used are environmentally friendly, providing consumers with trustworthy information about the products they buy.
3. Carbon Credit Tracking
DApps can also revolutionize the way carbon credits are tracked and traded. Blockchain’s immutable ledger ensures that carbon credits are transparently recorded and cannot be double-counted. This increases the reliability of carbon credit markets and encourages more businesses to participate in carbon offsetting programs.
Potential Benefits
- Reduction in Fraud: By using DApps for supply chain management, companies can reduce instances of fraud and misreporting. Every transaction and movement of goods is recorded on the blockchain, making it nearly impossible to alter records without detection.
- Increased Consumer Trust: With verifiable claims about sustainability, companies can build greater trust with consumers. Knowing that a product’s environmental claims are backed by blockchain data can influence purchasing decisions.
- Enhanced Regulatory Compliance: For industries that require rigorous environmental compliance, DApps can provide an automated and reliable way to ensure that all regulatory requirements are met and documented.
Challenges to Implementation
Despite these potential benefits, several challenges need to be addressed:
- Interoperability: Ensuring that DApps can communicate and operate across different blockchain platforms is crucial for widespread adoption.
- User Adoption: The success of DApps in promoting sustainability depends on their adoption by both businesses and consumers. Educating users about the benefits and usability of these applications is essential.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating the regulatory landscape for blockchain technology can be complex. Clear guidelines and supportive policies are needed to foster innovation while ensuring compliance.
Centralization vs. Decentralization
Traditional apps are typically managed by a single company, which controls the servers, data, and user interactions. In contrast, DApps operate on a decentralized network where the data is distributed across numerous nodes, making them more resistant to censorship and manipulation.
Transparency and Trust
One of the standout features of DApps is their transparency. Every transaction and change made on a DApp is recorded on a public ledger, usually a blockchain. This openness fosters a high level of trust among users, as they can verify the actions and integrity of the application themselves.
Security Enhancements
Because DApps run on a decentralized network, they are less vulnerable to traditional hacking attempts. There’s no central point of failure, which makes it significantly harder for malicious actors to compromise the system.
User Autonomy
DApps empower users by giving them full control over their data and digital assets. Users don’t have to rely on a central authority to manage their interactions, which fosters greater independence and self-sovereignty.
Conclusion
Decentralized applications hold immense potential not just in disrupting traditional industries but also in contributing to environmental sustainability. By focusing on energy efficiency, enhancing supply chain transparency, and revolutionizing carbon credit tracking, DApps can play a crucial role in building a greener future. As the blockchain ecosystem continues to evolve, it is imperative for developers, businesses, and regulators to collaborate in harnessing the power of DApps for environmental good.
FAQs
1. How do DApps promote energy efficiency?
DApps on energy-efficient blockchains like PoS reduce the carbon footprint compared to traditional PoW blockchains, thus promoting sustainable practices.
2. Can DApps ensure the authenticity of environmental claims by companies?
Yes, DApps can verify and record the provenance and sustainability of products on an immutable blockchain, ensuring the authenticity of environmental claims.
3. What role do DApps play in carbon credit markets?
DApps provide a transparent and immutable ledger for tracking and trading carbon credits, reducing fraud and increasing market reliability.
4. Are there any challenges in adopting DApps for environmental purposes?
Challenges include ensuring interoperability between different blockchains, increasing user adoption, and navigating regulatory hurdles.
5. What is the future of DApps in sustainability?
The future is promising as more energy-efficient blockchain solutions are developed and businesses increasingly recognize the value of transparency and trust in sustainability practices.
6. What makes DApps more secure than traditional apps?
DApps are more secure because they operate on a decentralized network, reducing the risk of a single point of failure. This makes it harder for hackers to target the system.
7. How can I start using DApps?
o start using DApps, you’ll need a digital wallet compatible with the blockchain network the DApp is built on. From there, you can access various DApps directly through your wallet.
8. What are some examples of real-world problems DApps can solve?
DApps can address issues like financial inclusion, by providing banking services to unbanked populations, and enhance transparency in supply chains, ensuring the authenticity of products and ethical sourcing.
By exploring these often overlooked aspects of DApps, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of their potential impact on our world. The intersection of blockchain technology and environmental sustainability is an exciting frontier that holds promise for significant positive change.