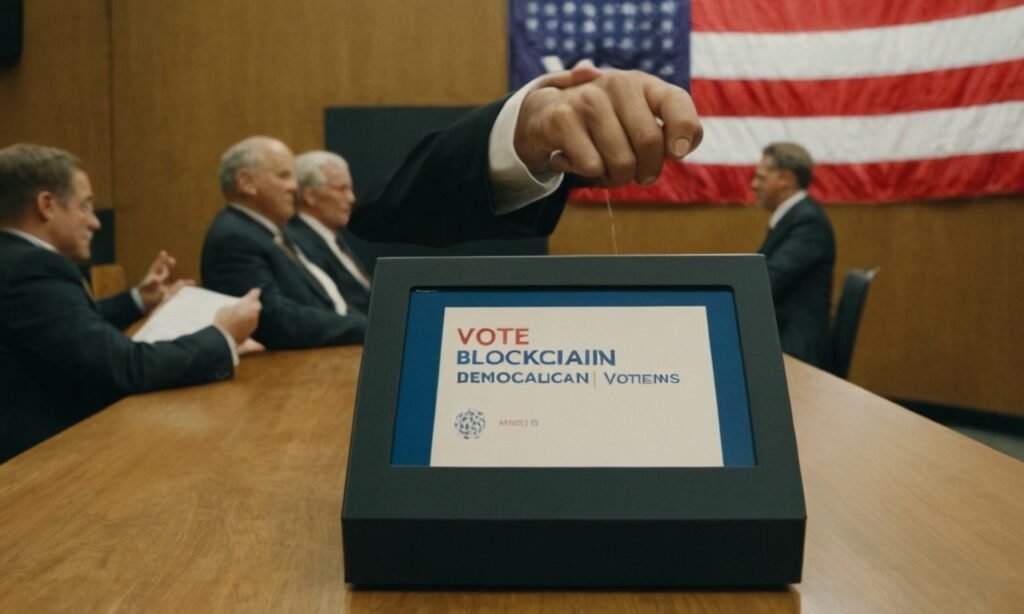
Discover how blockchain technology can revolutionize voting systems and democracy by providing enhanced security, transparency, and trust. Learn how this innovative approach addresses current challenges in the electoral process.
Introduction
Voting systems are the backbone of democratic societies, ensuring that citizens’ voices are heard and that leaders are chosen fairly. Yet, traditional voting systems are plagued with issues such as fraud, hacking, and lack of transparency. Enter blockchain technology—a game-changer that promises to address these challenges head-on. In this article, we’ll delve into how blockchain can enhance voting systems and democracy, making elections more secure, transparent, and trustworthy.
What is Blockchain?
Before diving into the nitty-gritty of how blockchain can revolutionize voting, let’s first understand what blockchain is. In simple terms, blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers in a way that ensures the data cannot be altered retroactively. This technology’s inherent features—decentralization, transparency, and immutability—make it an ideal candidate for enhancing voting systems.
The Current State of Voting Systems
Traditional voting systems, whether paper-based or electronic, have several vulnerabilities:
- Fraud and Tampering: Ballot stuffing, vote buying, and manipulation of electronic voting machines are just a few examples.
- Lack of Transparency: Voters often have to trust that the system works as intended without having a way to verify it themselves.
- Accessibility Issues: For many, especially those living abroad or with disabilities, voting can be a cumbersome process.
- Inefficiency: Manual counting of votes and other logistical hurdles can delay results and increase the risk of errors.
How Blockchain Can Enhance Voting Systems
Security and Fraud Prevention
One of the most significant advantages of blockchain is its robust security features. Each vote can be recorded as a block on the blockchain, making it nearly impossible to alter or delete once it’s added. This feature alone can drastically reduce the chances of fraud and tampering.
- Immutable Records: Votes recorded on a blockchain can’t be changed, ensuring the integrity of the electoral process.
- Cryptographic Security: Blockchain uses advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data, making it highly resistant to hacking.
- Decentralization: By distributing the ledger across many nodes, there’s no single point of failure that hackers can target.
Transparency and Trust
Transparency is another critical area where blockchain can make a massive impact. By allowing voters to independently verify their votes, blockchain can significantly increase trust in the voting process.
- Public Ledger: All transactions (votes) are recorded on a public ledger that anyone can inspect, fostering transparency.
- Voter Verification: Voters can check that their vote has been counted without compromising their anonymity.
- Auditability: Election officials can easily audit the election results, ensuring all votes are accounted for correctly.
Accessibility and Convenience
Blockchain can also make voting more accessible and convenient. With blockchain-based voting, people can vote from anywhere in the world using their smartphones or computers.
- Remote Voting: Expats, military personnel, and those with mobility issues can vote securely from their location.
- Ease of Use: Blockchain voting platforms can be designed to be user-friendly, encouraging higher voter turnout.
- Instant Results: Votes can be counted and verified quickly, providing near-instant election results.
Addressing Common Concerns
Privacy
One of the biggest concerns with blockchain voting is privacy. People worry that their votes could be traced back to them, compromising the principle of a secret ballot.
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs: These cryptographic methods allow one party to prove to another that a statement is true without revealing any additional information. This can be used to verify votes without revealing voter identities.
- Anonymous Voting: Blockchain can be designed to anonymize votes, ensuring that no one can trace a vote back to a specific individual.
Technical Challenges
Implementing blockchain voting isn’t without its technical challenges.
- Scalability: Blockchain networks need to handle millions of transactions quickly and efficiently.
- Digital Divide: Not everyone has access to the necessary technology or the skills to use it.
Regulatory and Legal Hurdles
Governments and regulatory bodies will need to adapt to this new technology.
- Legal Frameworks: New laws and regulations will be required to govern blockchain voting.
- Standardization: There must be standards in place to ensure the interoperability and security of blockchain voting systems.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Several countries and organizations have already started experimenting with blockchain voting.
Estonia
Estonia has been a pioneer in digital governance, and it’s no surprise that they are exploring blockchain voting. Their e-residency program and digital ID cards make it easier to implement such advanced systems.
West Virginia, USA
In 2018, West Virginia became the first U.S. state to use blockchain for a federal election, allowing military personnel stationed overseas to vote using a blockchain-based mobile app.
Switzerland
Swiss municipalities have also experimented with blockchain voting in local referendums, showing promising results in terms of security and voter confidence.
The Future of Voting with Blockchain
Increased Adoption
As more pilot projects succeed, we can expect a broader adoption of blockchain voting systems worldwide. The transparency and security offered by blockchain can help restore faith in democratic processes.
Technological Advancements
With ongoing advancements in blockchain technology, many current limitations will be addressed. Improved scalability solutions and user-friendly interfaces will make blockchain voting more practical and accessible.
Enhanced Democratic Participation
Blockchain voting can lead to higher voter turnout and more engaged citizens. By making voting more accessible and secure, people will be more inclined to participate in the democratic process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How does blockchain ensure the security of votes?
Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to secure votes. Once a vote is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, making it highly resistant to tampering and fraud.
2. Can blockchain voting ensure voter anonymity?
Yes, blockchain can be designed to ensure voter anonymity through techniques like zero-knowledge proofs and anonymous voting protocols, ensuring that votes cannot be traced back to individuals.
3. Is blockchain voting scalable?
While scalability is a challenge, ongoing advancements in blockchain technology are addressing these issues, making it possible to handle millions of transactions quickly and efficiently.
4. What are the legal implications of blockchain voting?
Governments will need to create new legal frameworks and standards to govern blockchain voting systems, ensuring they are secure, interoperable, and compliant with existing laws.
5. How can blockchain improve voter turnout?
By making voting more accessible and convenient, blockchain can encourage more people to participate in elections. Remote voting options and user-friendly platforms can significantly boost voter turnout.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology holds immense potential to enhance voting systems and democracy. Its security, transparency, and accessibility features can address many of the issues plaguing traditional voting systems. While there are challenges to overcome, the benefits of blockchain voting are too significant to ignore. As we continue to innovate and adapt, we can look forward to a future where every vote is secure, transparent, and trustworthy.
In the grand scheme of things, how blockchain can enhance voting systems and democracy is just the tip of the iceberg. This technology can fundamentally transform the way we think about governance and civic engagement, ushering in a new era of democratic participation. So, let’s embrace this innovation and work towards a brighter, more democratic future!