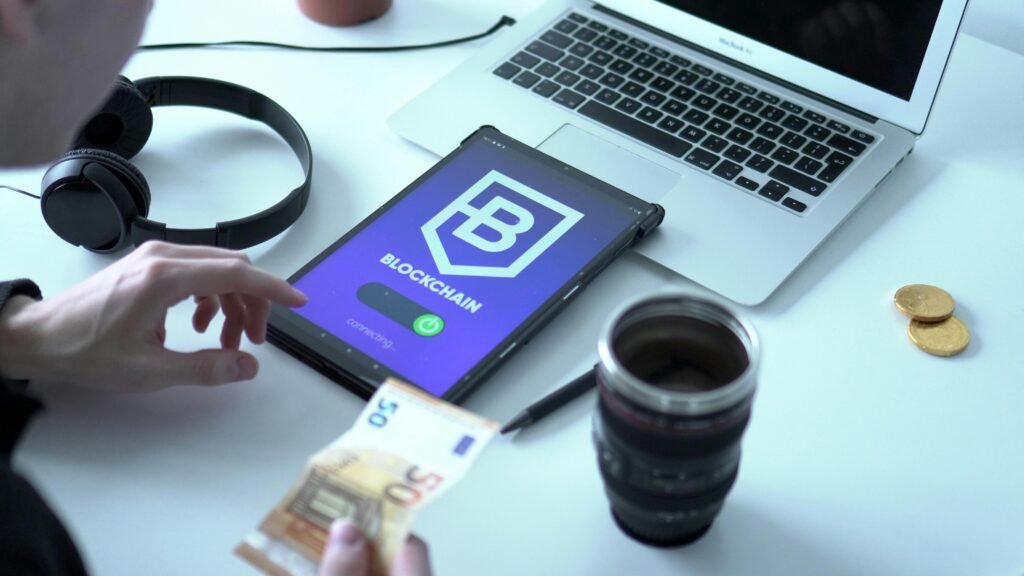
The intersection of blockchain technology and digital identity is a rapidly evolving landscape, offering groundbreaking solutions to modern challenges in identity verification and management. While many articles cover the basic benefits, applications, and challenges, there’s a nuanced aspect that often goes unmentioned: the implications of decentralized identity systems for marginalized populations and the unbanked. Let’s explore this in detail.
Empowering the Marginalized and Unbanked with Blockchain
1. Addressing Identity Gaps
Millions of people worldwide lack any form of official identification, which restricts their access to essential services like banking, healthcare, and education. Blockchain technology can offer a self-sovereign identity system where individuals control their personal data and can create a verifiable identity without the need for a centralized authority.
2. Inclusivity and Accessibility
Decentralized identity systems can be particularly transformative for marginalized groups. These systems do not require an intermediary, thus reducing the barriers to obtaining a recognized identity. This is especially beneficial in regions where government-issued IDs are hard to come by due to logistical, political, or social issues .
3. Financial Inclusion
Blockchain-based identities can facilitate financial inclusion for the unbanked by providing a reliable form of identity verification that financial institutions can trust. This can open up access to banking services, microloans, and other financial tools that are otherwise inaccessible.
4. Empowerment through Ownership
With blockchain, individuals own their data. This means they can decide who gets access to their information and how it is used. For marginalized communities, this is a significant shift from being passive recipients of services to active participants in their own identity management.
5. Reducing Fraud and Exploitation
Decentralized identity systems reduce the risk of fraud and exploitation by ensuring that personal data cannot be altered or tampered with once it is recorded on the blockchain. This enhances trust and security, which is crucial for vulnerable populations who are often targets of identity theft and fraud.
Challenges to Overcome
1. Technological Barriers
Despite the potential, the adoption of blockchain-based identity systems faces significant technological barriers. Access to digital infrastructure and digital literacy are essential for the effective use of these systems, which can be a hurdle in underdeveloped regions.
2. Interoperability Issues
Creating interoperable systems that can work across different platforms and jurisdictions is a complex task. This is necessary to ensure that blockchain-based identities are universally accepted and recognized.
3. Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
The implementation of blockchain for digital identities requires robust legal and regulatory frameworks to ensure privacy, security, and compliance with international standards.
4. Public Trust and Adoption
Building public trust in decentralized identity systems is essential. Educating communities about the benefits and security of blockchain-based identities is necessary to drive adoption.
Conclusion
The potential of blockchain technology to revolutionize digital identity management is immense, particularly for marginalized and unbanked populations. By providing a secure, decentralized, and self-sovereign identity system, blockchain can empower millions who currently lack access to essential services. However, realizing this potential requires overcoming significant technological, regulatory, and educational challenges. As the technology evolves, it holds the promise of creating a more inclusive and secure digital world.
FAQs
1. What is a self-sovereign identity?
A self-sovereign identity is a digital identity that is owned and controlled entirely by the individual, without the need for a centralized authority.
2. How does blockchain enhance security in digital identities?
Blockchain enhances security through immutable and encrypted data storage, ensuring that personal data cannot be tampered with once recorded.
3. Can blockchain help the unbanked access financial services?
Yes, blockchain-based identities can provide the necessary verification for the unbanked to access banking services and financial tools.
4. What are the main challenges in adopting blockchain for digital identity?
Key challenges include technological barriers, interoperability issues, legal and regulatory hurdles, and building public trust and adoption.
5. How can decentralized identities benefit marginalized communities?
Decentralized identities can provide reliable and verifiable identities to those without official identification, enhancing access to essential services and reducing the risk of fraud and exploitation.
By focusing on these overlooked aspects, we can better understand and harness the transformative potential of blockchain technology in digital identity management.